Heat pumps are a staple in many households in the U.S. Many power their homes using gas but are looking to switch to heat pumps. However, they are unsure how much electricity or power a heat pump might consume.
Heat pumps are versatile because they provide heat in the winter, help keep cool in the summer, and even provide hot water. They are also a sustainable way of saving energy in the home.
A heat pump distributes heat from the outside air to the building’s interior. It can also be used to cool a house by transferring hot indoor air to the outside.
Moreover, a heat pump does not use a lot of electricity. Because they are energy-efficient, they have less of an effect on your electricity bill. Using ductless heat pumps can mean tax credit or rebate eligibility because they are environmentally friendly.
Key Takeaways
– Heat pumps use less electricity than traditional systems, but they still consume a significant amount of power. Some factors that affect how much electricity a heat pump uses include: size, climate, efficiency, and more.
– Heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another. In the summer, they transfer heat from your home to the outside air. In the winter, they transfer heat from the outside air into your home.
– Because heat pumps move heat instead of creating it, they are very efficient. They use about 50% less electricity than traditional heating and cooling systems.
Table of Contents
- How many watts does a heat pump use?
- How much electricity does a heat pump use per day?
- Is it cheaper to run a heat pump all the time?
- How much electricity does a heat pump use per month?
- What is a heat pump?
- How a heat pump works?
- Benefits of using a heat pump
- How to lower the electric bill for a heat pump
- Combining a heat pump with solar energy
- Final thoughts

How many watts does a heat pump use?
The answer is: it depends. The size of the heat pump and the temperature outside will affect how many watts the heat pump uses. Generally speaking, a 1-ton heat pump will use about 1,200 watts of power. But if it’s a cold day and the heat pump is working hard to maintain a comfortable temperature inside, it could use closer to 2,000 watts.
How much electricity does a heat pump use per day?
If you’re considering a heat pump for your home, you may be wondering about the cost of running one. Here’s a look at how much electricity a heat pump uses per day, on average.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, a typical home heat pump will use about 3,500 watts of electricity per day. That’s about 30 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per day, or just over 1,000 kWh per month.
Of course, the actual amount of electricity your heat pump uses will depend on a number of factors, including the size and efficiency of your unit, the climate you live in, and how often you use it. But as a general rule of thumb, you can expect to pay about $30-$40 per month for heat pump electricity usage.

Is it cheaper to run a heat pump all the time?
With the cost of electricity on the rise, many people are looking for ways to cut back on their energy consumption. One question that often comes up is whether it is cheaper to run a heat pump all the time or only when needed.
There are a few factors to consider when answering this question. First, how much does it cost to run the heat pump? Second, how much does it cost to heat your home using other methods? And finally, how often do you need to use the heat pump?

Taking all of these factors into account, it is usually cheaper to run a heat pump all the time. The initial cost of purchase and installation can be offset by the savings on your energy bill. Additionally, you will avoid the hassle and expense of having to turn on and off your heat pump every time the weather changes.
How much electricity does a heat pump use per month?
A heat pump uses about 1,500 watts of electricity to operate. This means that, on average, a heat pump will use about 12 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per day, or 360 kWh per month.
The actual amount of electricity a heat pump uses will vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the unit, the climate it is used in, and how often it is used. However, on average, a heat pump will use about 1,500 watts of electricity to operate.
So how much does this translate into on your monthly electric bill? Well, it depends on the rate you pay for electricity. For example, if you pay 10 cents per kWh, then your monthly bill for operating a heat pump would be $36.00.
What is a heat pump?
Heat pumps use electricity and refrigeration to heat and cool spaces. Being made up of condensers and indoor units makes it a “two-component system.”
While the indoor unit operates inside the house, the condenser is located outside and heats or cools it. The indoor unit is usually mounted on the wall and distributes hot or cold air all through the house.
There are three types of heat pumps: ground, air, and water source. The names describe where the system absorbs heat from; thus, each works differently.
A heat pump may also be referred to as a mini-split. It earned this name because a refrigerant line splits the condenser and the indoor unit. Heat pumps have gradually become the preferred choice for heating and cooling. In addition, the efficiency rate of a heat pump is high, and you do not need ductwork in your home to use it.
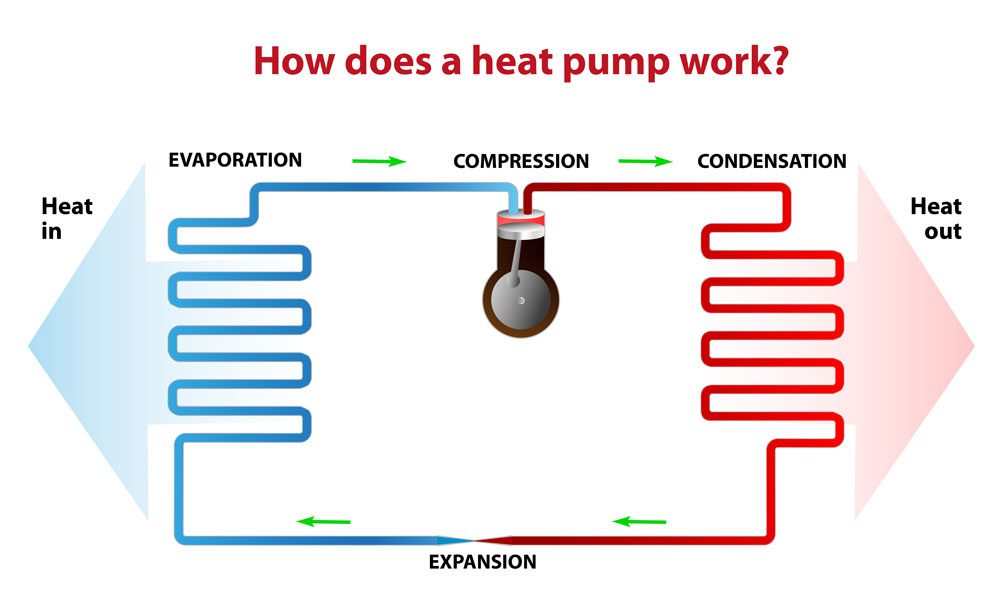
How a heat pump works?
A heat pump delivers heat from one room to the next using electricity and refrigerant. The refrigerant collects heat from the ground, air, or water and changes from liquid to gas. Next, the gas compresses and increases in temperature before moving to the indoor unit. As this happens, air passes over the refrigerant and goes out of the indoor unit as heat.
You can control the indoor unit thermostatically. When you need heat, the fan outside draws in hot air, which the refrigerant line carries to the indoor unit. A fan inside the unit then transfers the heat to your home. The reverse happens when in cooling mode.
A ground-source heat pump uses a solution-filled pipe to extract heat from the ground. An air-source heat pump absorbs heat using an outdoor fan. Finally, a water-source heat pump takes water from pipes laid in a water source. But you can do this only if you have a large body of water around your house. If the volume of water is not large enough, the water temperature can drop, thus causing it to freeze.
Benefits of using a heat pump
A heat pump needs electricity to power it up, but electricity is not used to generate heat. Thus, its efficiency rate is remarkably high.
With a space heater or electric baseboard, one unit of heat is used per unit of electricity for 100% efficiency. However, with a heat pump, the efficiency is tripled. A heat pump can provide three heating units for every unit of electricity consumed. This brings its efficiency rate up to 300%.
When using a heat pump, the electricity consumed is only used to power the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and pump. The way the heat pump works offers convenience and lower electricity bills. Heat pump usage only increases your electricity bill by a monthly average of $75.
The heating system may be electric, gas, oil, or a combination. You will have to use this method annually, reducing your heating fuel bill. The COP measures the efficiency of a heat pump. The COP is the relationship between electricity (power supplied) and heat (power drawn out). A heat pump with a COP of three can generate three units of cooling or heating power for every unit of electricity used in the system.
Regardless, a heat pump’s COP depends on some factors. The quality of installation, type of heat pump, and refrigerant can affect COP. Generally, if the COP of your heat pump is above one, you may consider your heat pump’s efficiency.
Another factor affecting output is the size of your house. Typically, the bigger your house, the higher the output of your heat pump. A general guide says that for a three-bedroom house, the recommended output is five kW. A typical house uses about 12 kWh of heat annually. Thus, a COP of three means your heat pump would use four kW of electricity annually. With a higher COP, a heat pump would use less electricity. However, the output of your house also depends on the climate and insulation quality.
How to lower the electric bill for a heat pump
You may notice a hike in your electricity consumption when you switch to a heat pump. However, your utility bill will be reduced. But there are ways to reduce your bills and energy consumption as well.

- First, ensure the water heating temperature is around 40°C or less. The higher your heat pump is set, the more power it will consume to get the suitable temperature.
- Second, try to set your house thermostat to a constant. Frequent changes in the temperature mean more power usage by your heat pump. But maintaining the same temperature will cause it to use less power. Also, lowering your thermostat by just one degree can cause a 2.5% reduction in your energy bill.
- Third, ensure you clean your heat pump filter and fans routinely. A clogged filter will allow less air to pass through, lowering performance. Additionally, it would be best if you got service done for your heat pump annually.
- Finally, combining it with solar energy is one of the most efficient ways to use less electricity with a heat pump. The use of solar panels can reduce your heat pump’s running costs by 40%.
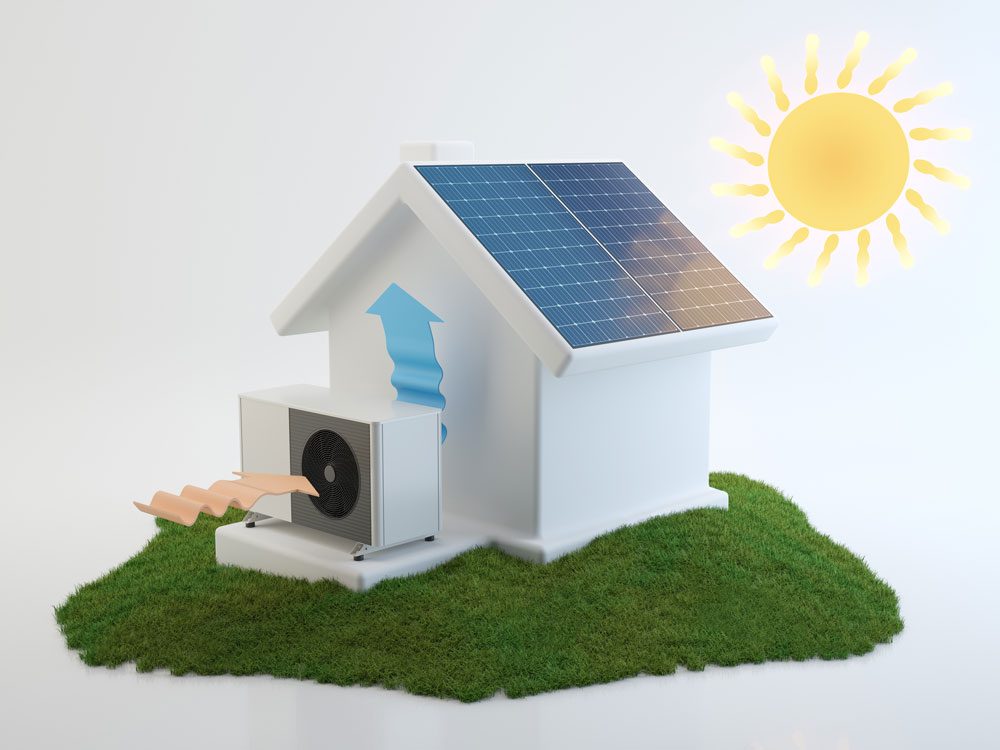
Combining a heat pump with solar energy
Because of how it gathers heat, a heat pump can be used in many ways to save power. The heat pump cannot generate heat; instead, it collects the heat in the atmosphere and pumps it into your home. This mechanism makes it more efficient than traditional heating systems. Thus, a heat pump combined with other energy-saving measures can significantly impact your bills.
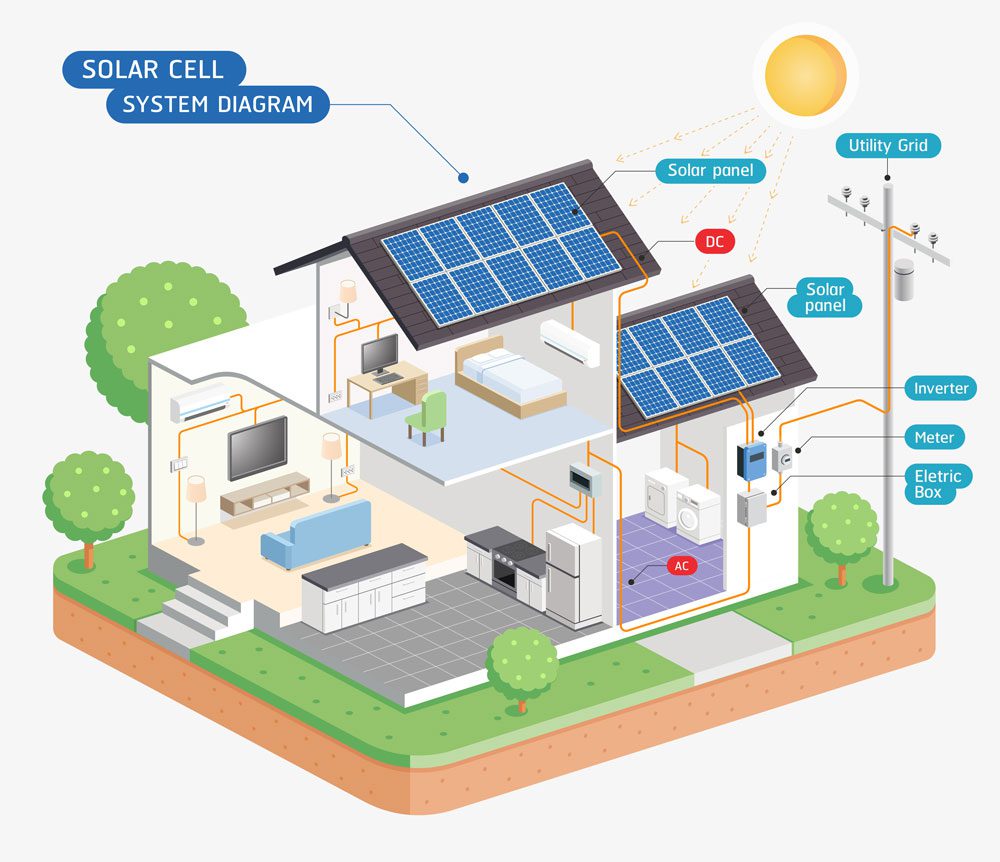
Solar power can help you reduce your carbon footprint even further. Also, if you put solar panels on your home, they can help you generate electricity. Your utility company can credit that electricity back to you, and you can sell the electricity you harnessed back to the grid. This offset can dramatically reduce your monthly utility bill.
When you combine solar and heat pumps, you can reduce the power used for heating from 14.5 cents per kWh to 9 cents per kWh. Your running cost for the heat pump thus decreases by about 40% annually.
Considering that heat pumps are about 50% less expensive than gas heating, adding solar panels can save you money. Plus, you start to rely less on external energy. Your home may effectively become self-sufficient over time using this combination.
Final thoughts
A heat pump is a sustainable option that every home should consider. Since it uses existing heat, it can consume less electricity. A heat pump has excellent advantages over traditional gas heating.
Using a heat pump, you can reduce your home’s oil consumption by about 300 gallons. The electricity a heat pump uses is less than gas heating costs. Thus, switching to a heat pump immediately affects your utility bill.
It is possible for heat pumps to achieve an efficiency rate of over 300%. Compared to a gas boiler with an efficiency of 95%, it is a no-brainer. In addition, a heat pump can help to reduce your carbon footprint by combining it with solar energy.
Using solar energy and a heat pump, you are on your way to building a self-sufficient home. To get the most out of your heat pump, you should clean it often, keep your thermostat at the same temperature, and lower the water heating temperature.
With these best practices, your heat pump should function perfectly, and you can avoid surges in your utility bill.


