Safeguard Your Home and Comfort with Our Expert Guide on Freon Leaks
A Freon leak in your home can pose serious health risks and environmental concerns. As a homeowner, it’s crucial to understand the causes, signs, and solutions related to Freon leaks. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of Freon and refrigerants, discuss how to detect and diagnose leaks, explore repair and prevention strategies, and consider the importance of hiring a licensed HVAC technician. Our goal is to provide you with expert, authoritative, and trustworthy information to ensure a safe and efficient home environment.
Key Takeaways
- Freon leaks in residential HVAC systems can lead to health risks, environmental impact, and reduced cooling efficiency.
- Common causes of refrigerant leaks include damaged or corroded components, loose or faulty connections, and Schrader valves.
- To detect and diagnose a Freon leak, use various methods such as electronic leak detectors, UV dye, soap bubble tests, infrared cameras, and vacuum tests.
- Hire a licensed HVAC technician to repair or replace damaged components, recover and dispose of refrigerants properly, and perform preventative maintenance to minimize the risk of future leaks.
- Retrofitting and upgrading HVAC systems can improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of refrigerant leaks.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of your HVAC system are essential to prevent refrigerant leaks and extend the life of your equipment.
Table of Contents
- Safeguard Your Home and Comfort with Our Expert Guide on Freon Leaks
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Freon and Refrigerants
- Causes and Signs of a Freon Leak
- Detection and Diagnosis of Freon Leaks
- Repair, Replacement, and Prevention
- Environmental and Health Considerations
- Choosing a Licensed HVAC Technician
- FAQ
- Conclusion

Understanding Freon and Refrigerants
Freon is a trade name for a class of refrigerants used in air conditioning, refrigeration, and heat pump systems. These refrigerants fall into different chemical categories, including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), both of which have detrimental environmental effects.
Environmental Impact of Refrigerant Leaks
Refrigerant leaks, especially those involving chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), have significant consequences on the environment. The two main environmental concerns associated with these refrigerants are ozone depletion and global warming.
Ozone Depletion
The Earth’s ozone layer, situated in the stratosphere, serves as a protective barrier against harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. CFCs and HCFCs, once released into the atmosphere, break down and release chlorine atoms, which react with ozone molecules. This reaction depletes the ozone layer, allowing more UV radiation to reach the Earth’s surface. Increased exposure to UV radiation can lead to a range of issues, including:
- Skin cancer
- Cataracts
- Suppressed immune systems
- Disruption of marine and terrestrial ecosystems
In response to the global threat posed by ozone depletion, the Montreal Protocol was established in 1987. This international treaty aims to phase out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances, including CFCs and HCFCs.
Global Warming
In addition to their ozone-depleting properties, refrigerants like CFCs and HCFCs are also potent greenhouse gases. When released into the atmosphere, these substances trap heat and contribute to global warming. The global warming potential (GWP) of a substance is a measure of its heat-trapping ability relative to that of carbon dioxide (CO2). CFCs and HCFCs have a much higher GWP than CO2, making them significant contributors to climate change.
To mitigate the impact of refrigerants on global warming, alternative refrigerants with lower GWP values have been developed. Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), for example, have a reduced GWP compared to CFCs and HCFCs, and are increasingly being used as a more environmentally friendly option. However, even HFCs can contribute to global warming, so further research and development of new, sustainable refrigerants continue to be a priority.
Health Risks Associated with Freon Leaks
Exposure to high levels of refrigerants, such as Freon, can pose various health risks. Inhaling refrigerants can lead to the displacement of oxygen in the air, resulting in a range of symptoms depending on the level and duration of exposure. The following are some potential health issues associated with exposure to refrigerants:
- Headaches: Exposure to refrigerants may cause headaches due to a lack of oxygen or irritation of the respiratory system.
- Dizziness: Inhaling refrigerants can lead to dizziness, possibly resulting from reduced oxygen levels in the brain or direct effects on the central nervous system.
- Respiratory irritation: Freon and other refrigerants can irritate the respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath (Source).
- Heart problems in severe cases: In extreme cases, exposure to high levels of refrigerants may cause heart palpitations or arrhythmias, which can be life-threatening if not promptly addressed.
It is essential to minimize the risk of exposure to refrigerants by ensuring proper ventilation and taking appropriate safety measures when handling these substances.
Common Refrigerants Used in Residential HVAC Systems
Various types of refrigerants are used in residential heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Over time, the industry has transitioned from ozone-depleting refrigerants to more environmentally friendly alternatives. Here are two common refrigerants found in residential HVAC systems:
- R-22 refrigerant: An HCFC refrigerant, commonly known as Freon, R-22 was widely used in older residential air conditioning systems. Due to its ozone-depleting properties, R-22 production and importation have been phased out under the Montreal Protocol and the U.S. Clean Air Act.
R-410A refrigerant: As an environmentally friendlier hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant, R-410A is commonly used in newer air conditioning systems. It does not contribute to ozone depletion, making it a more sustainable choice compared to R-22. However, it still has a global warming potential, which has led to ongoing efforts to develop even more eco-friendly refrigerants.
From then, appliance manufacturers are urged to substitute Freon with a more environmentally friendly gas which is R-410A refrigerant. Most appliances manufactured after 2005 are unlikely to have Freon, and those made after 2010 aren’t allowed by law to have Freon.
Do You Know Which Appliances Use Freon?
Freon is a type of refrigerant that is used in a variety of appliances, including air conditioners, refrigerators, and freezers. Freon is also used in some food processors.
Freon is known for its ability to cool and dehumidify air, making it an ideal choice for use in appliances that need to maintain a consistent temperature.
Causes and Signs of a Freon Leak
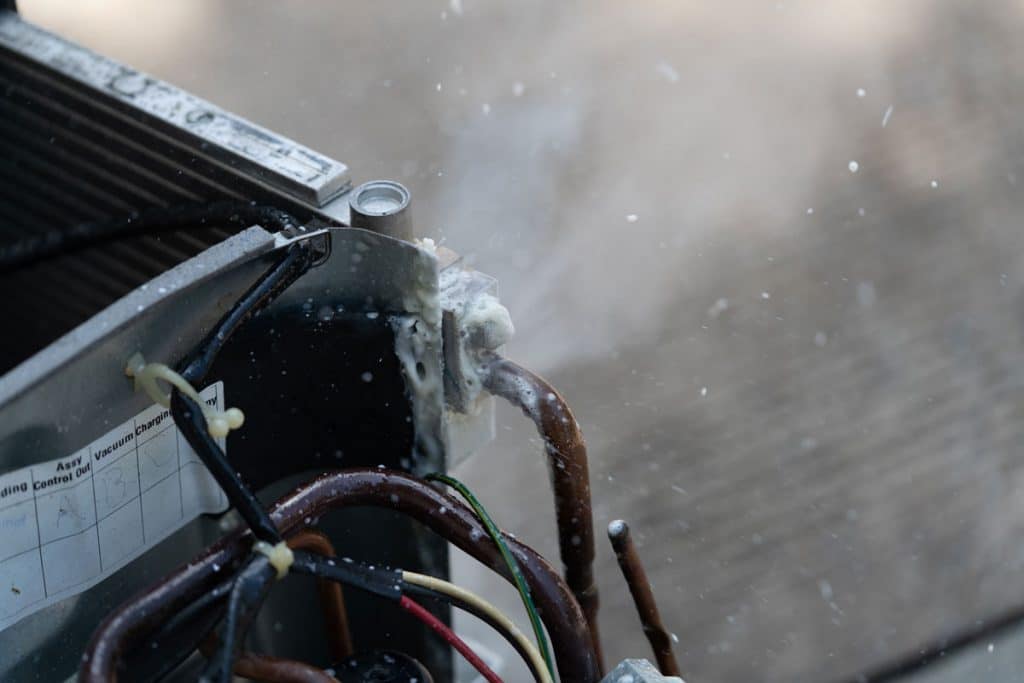

Understanding the common causes and signs of a Freon leak is essential for quick detection and resolution. This enables homeowners to take the necessary steps to address the issue and prevent potential health hazards or damage to the HVAC system.
Common Causes of Refrigerant Leaks
- Damaged or corroded components: Over time, the metal components of an HVAC system may become corroded, leading to refrigerant leaks. Corrosion can be caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or other environmental factors.
- Loose or faulty connections: Poorly fitted or loose connections between components can result in refrigerant leaks. This may occur due to manufacturing defects, improper installation, or wear and tear.
- Schrader valves: These valves are used in HVAC systems to control the flow of refrigerant. Leaks can occur if the valve is damaged or if the valve cap is not adequately tightened.
Identifying Signs of a Freon Leak
- Reduced cooling efficiency: When refrigerant levels are low due to a leak, the HVAC system may struggle to cool the air effectively, leading to reduced cooling efficiency.
- Hissing or bubbling noises: A hissing or bubbling noise may be heard near the location of the leak, as refrigerant escapes from the system.
- Ice formation on the evaporator coil: Low refrigerant levels can cause the evaporator coil to freeze, resulting in ice formation. This may be an indication of a Freon leak.
- Unusual chemical smell: Freon and other refrigerants have a distinct chemical odor. If you notice an unusual smell around your HVAC system, it may be due to a refrigerant leak.
Source and more information available: U.S. Department of Energy – Common Air Conditioner Problems: Link
Detection and Diagnosis of Freon Leaks
To accurately detect and diagnose a Freon leak, various methods and tools can be employed.
Leak Detection Methods
- Electronic leak detectors: Devices designed to detect refrigerant leaks by sensing the presence of refrigerant gases in the air.
- Ultraviolet (UV) dye: A fluorescent dye added to the refrigerant, which becomes visible under UV light when a leak is present.
- Soap bubble tests: A solution of soap and water applied to suspected leak areas, which produces bubbles if a leak is present.
- Infrared cameras: Devices that detect temperature differences to identify potential leaks.
Vacuum Test
A vacuum test is performed by an HVAC technician to ensure the integrity of an HVAC system and detect any leaks. The process involves placing the system under a vacuum and monitoring for pressure changes.
Systematic Approach to Leak Detection and Diagnosis
A methodical process should be followed to identify, diagnose, and repair refrigerant leaks in order to maximize efficiency and safety. This includes inspecting all system components, performing a vacuum test, and using the appropriate leak detection methods.
DIY vs. Professional Service
While some homeowners may attempt to locate and repair refrigerant leaks themselves, it’s generally recommended to hire a licensed HVAC technician. Professionals have the necessary tools, expertise, and certifications to handle refrigerants safely and effectively. Additionally, attempting DIY repairs may void your system’s warranty or cause further damage.
Repair, Replacement, and Prevention
Once a Freon leak has been detected and diagnosed, the next step is to repair or replace the affected components and implement prevention strategies.
Repairing or Replacing Damaged Components
An HVAC technician can evaluate the severity of the leak and recommend the appropriate course of action, which may involve repairing the damaged component or replacing the entire system.
Refrigerant Recovery and Proper Disposal
Before repairing or disposing of an appliance, it’s essential to safely remove the refrigerant. HVAC technicians are trained and certified to handle refrigerant recovery and ensure proper disposal in compliance with EPA regulations.
Retrofitting and Upgrading HVAC Systems
Retrofitting involves upgrading existing HVAC systems to use environmentally-friendly refrigerants and improve energy efficiency. This process may involve replacing certain components or converting the system to operate with alternative refrigerants.
Preventative Maintenance and Leak Prevention Strategies
Regular inspection and upkeep of HVAC systems can minimize the risk of refrigerant leaks and extend the life of the equipment. Preventative maintenance may include:
- Tightening connections
- Inspecting and replacing worn components
- Monitoring refrigerant levels
- Cleaning coils and filters
Warranty Considerations and Cost Factors
Understanding the terms of your HVAC system’s warranty is crucial when dealing with refrigerant leaks. Repairs or replacements related to refrigerant leaks may be covered, depending on the warranty terms. Additionally, consider the financial impact of addressing a refrigerant leak, including repair or replacement costs and potential energy savings from improved system efficiency.
Environmental and Health Considerations
As a homeowner, it’s important to prioritize environmental responsibility and ensure a healthy living environment.
EPA Regulations and Refrigerant Management Plans
Following guidelines and requirements set forth by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for handling, disposing, and recycling refrigerants is essential. Implementing a comprehensive refrigerant management plan can help maintain HVAC systems, track refrigerant usage, and ensure compliance with EPA regulations.
Reducing Carbon Footprint Through Proper Maintenance
By addressing refrigerant leaks and properly maintaining HVAC systems, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier environment.
Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
Maintaining good indoor air quality is vital for overall health and well-being. Ensuring proper ventilation and airflow in living spaces can help mitigate the effects of a refrigerant leak and maintain healthy indoor air quality.
Safety Precautions When Handling Refrigerants
Taking the necessary precautions when dealing with refrigerants is essential for minimizing potential hazards. Safety measures may include wearing protective gear, ensuring proper ventilation, and following guidelines for handling and disposing of refrigerants.
Air Conditioning Alternatives and Energy Efficiency
Exploring alternative cooling options, such as evaporative coolers or ductless mini-split systems, can reduce refrigerant-related risks and environmental impact. Additionally, selecting energy-efficient HVAC systems or appliances can help lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing a Licensed HVAC Technician
Hiring a licensed HVAC technician is crucial for addressing refrigerant leaks and ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your HVAC system.
Importance of Hiring a Certified Professional
Certified HVAC technicians have the necessary training, experience, and certifications to handle refrigerants and perform maintenance, repair, or installation of HVAC systems.
Technician Certifications and Qualifications
Look for professionals with recognized certifications, such as North American Technician Excellence (NATE) or HVAC Excellence, as these demonstrate a technician’s competency in handling refrigerants and HVAC systems.
Tips for Selecting a Reliable HVAC Service Provider
When choosing an HVAC technician, consider factors such as:
- Experience and certifications
- Customer reviews and recommendations
- Responsiveness and communication
- Warranty and insurance coverage
- Transparent pricing and estimates
FAQ
Can a Freon leak in my home be dangerous?
A Freon leak can pose potential health risks if exposed to high levels of refrigerant for an extended period. Symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, respiratory irritation, and, in severe cases, heart problems. It is crucial to address a refrigerant leak promptly to minimize any health risks.
How do I know if my HVAC system has a Freon leak?
Signs of a Freon leak in your HVAC system may include reduced cooling efficiency, hissing or bubbling noises, ice formation on the evaporator coil, and an unusual chemical smell. If you suspect a leak, it’s essential to call a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and repair the issue.
Can I fix a Freon leak myself?
While some homeowners may attempt DIY repairs, it is generally recommended to hire a licensed HVAC technician to handle refrigerant leaks. Professionals have the necessary tools, expertise, and certifications to handle refrigerants safely and effectively. DIY repairs may void your system’s warranty or cause further damage.
How can I prevent Freon leaks in my HVAC system?
Regular preventative maintenance is key to minimizing the risk of refrigerant leaks and extending the life of your HVAC system. This may include tightening connections, inspecting and replacing worn components, monitoring refrigerant levels, and cleaning coils and filters.
What is the environmental impact of refrigerant leaks?
Refrigerant leaks can contribute to ozone depletion and global warming. CFCs and HCFCs, such as Freon, are known to deplete the Earth’s ozone layer and are potent greenhouse gases. Newer refrigerants, such as HFCs, have less impact on the ozone layer but may still contribute to global warming.
Conclusion
| Topic | Description |
| Causes of Freon Leaks | Damaged or corroded components, loose or faulty connections, Schrader valves |
| Signs of Freon Leaks | Reduced cooling efficiency, hissing or bubbling noises, ice formation on evaporator coil, unusual chemical smell |
| Leak Detection Methods | Electronic leak detectors, UV dye, soap bubble tests, infrared cameras, vacuum tests |
| Repair and Replacement | HVAC technician evaluation, repair or replacement of damaged components, refrigerant recovery and proper disposal |
| Retrofitting and Upgrading | Upgrading HVAC systems for environmentally-friendly refrigerants and improved energy efficiency |
| Preventative Maintenance | Tightening connections, inspecting and replacing worn components, monitoring refrigerant levels, cleaning coils and filters |
| Environmental Impact | Ozone depletion, global warming |
| Health Risks | Headaches, dizziness, respiratory irritation, heart problems in severe cases |
Addressing Freon leaks in your home is crucial for maintaining a safe, healthy, and efficient living environment. By understanding the causes, signs, and solutions related to Freon leaks, you can take appropriate action and prioritize environmental responsibility. Don’t hesitate to consult with a licensed HVAC technician for expert guidance and professional service. With proper care and maintenance, you can ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your HVAC system, reduce your carbon footprint, and create a comfortable home for you and your family.


